Infraspinatus Anatomy
Updated:
The infraspinatus muscle is a crucial component of the shoulder complex, playing a vital role in the stability and movement of the shoulder joint. In this article, we will explore the infraspinatus anatomy, including its origin, insertion, action, function, nerve supply, blood supply, palpation techniques, clinical relevance, common injuries, and provide a list of useful links to relevant articles on physioadvisor.com.au. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of the infraspinatus muscle!
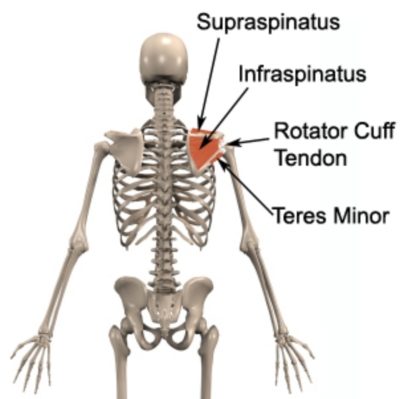
Origin and Insertion
The infraspinatus muscle arises from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula, which is located on the posterior aspect of the shoulder blade. From its origin, the muscle fibers converge and form a tendon that attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus, specifically the posterior facet.
Action and Function
The primary action of the infraspinatus muscle is to externally rotate the shoulder joint. It also contributes to the stabilization of the humeral head within the glenoid fossa during arm movements. Additionally, the infraspinatus muscle assists in the horizontal abduction of the shoulder, which involves moving the arm away from the midline of the body.
Nerve Supply and Blood Supply
The infraspinatus muscle receives its nerve supply from the suprascapular nerve, which arises from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. This nerve plays a vital role in innervating the muscles that control shoulder movements. In terms of blood supply, the infraspinatus muscle receives nourishment from branches of the suprascapular artery.
Infraspinatus Anatomy – Palpation
Palpating the infraspinatus muscle can provide valuable insights into its condition and potential dysfunctions. To palpate this muscle, locate the scapular spine and move your fingers laterally towards the posterior aspect of the shoulder joint. The infraspinatus muscle will be felt as a thick band of muscle fibers.
Infraspinatus Anatomy – Clinical relevance:
The infraspinatus muscle is frequently implicated in various shoulder pathologies. Some common injuries or conditions affecting this muscle include rotator cuff tears, tendinitis, impingement syndrome, and frozen shoulder. These conditions can cause pain, limited range of motion, and functional limitations, often requiring appropriate rehabilitation and physiotherapy interventions.
Useful PhysioAdvisor Links:
- “Rotator Cuff Tear: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment”
- “Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Rehabilitation”
- “Frozen Shoulder: Causes, Symptoms, and Management”
Infraspinatus Anatomy – Conclusion:
Understanding the infraspinatus anatomy is crucial for grasping its role in shoulder function and diagnosing associated pathologies. From its origin and insertion to its action, function, nerve supply, and blood supply, each aspect provides valuable insights into the importance of this muscle. By familiarizing ourselves with the infraspinatus and its clinical relevance, we can better appreciate the complexities of the shoulder joint and effectively address any issues that may arise. For more in-depth information on related topics, the links provided to physioadvisor.com.au articles offer a wealth of additional resources.
References:
- Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2017.
- Standring S, editor. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. Elsevier; 2016.
- Infraspinatus Muscle by KenHub.

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/infraspinatus-anatomy”>Infraspinatus Anatomy – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>Learn about infraspinatus anatomy including origin, insertion, action, innervation, blood supply, palpation, clinical relevance and more...
Return to the top of Infraspinatus Anatomy.
