Throwing Injuries
Updated:
Throwing injuries occur in throwing sports, such as cricket, baseball, softball, water polo, javelin and American football (quarterbacks). These injuries are typically due to overuse, presenting gradually overtime and are often associated with poor throwing technique. Throwing injuries tend to occur in the upper limb of the throwing arm, with pain most commonly occurring in the shoulder or elbow.

Most Common Throwing Injuries
Shoulder
Rotator Cuff Tear
Tearing of one or more rotator cuff muscles or their respective tendons (figure 1), typically following a forceful throw or a fall onto the shoulder or outstretched arm. Associated with pain in the shoulder that may radiate into the upper arm and sometimes pain on firmly touching the affected rotator cuff muscle or tendon (figure 1). Pain may also increase during throwing, lifting activities (especially with the arm outstretched or above the head), certain other shoulder movements (often overhead activities), when weight bearing through the affected arm or when lying on the affected side.
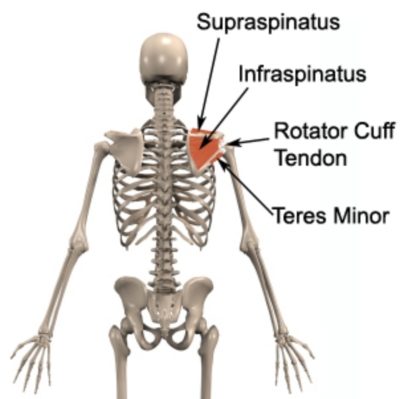
Figure 1 – Rotator Cuff Anatomy

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
SLAP Lesion
Damage to the cartilage lining the shoulder joint (labrum – figure 2) sometimes following overuse (such as excessive throwing), but often in association with a dislocated shoulder, a fall onto the arm or following a forceful throw. Pain is usually deep, although may present as vague shoulder pain. A clicking or catching sensation is often present during certain movements. Symptoms may increase with certain, often very specific movements or activities using the shoulder, such as cocking, acceleration or the release phase of throwing, during arm elevation or lifting (especially overhead), weight bearing through the affected arm (e.g. push ups) or sometimes lying on the affected side.
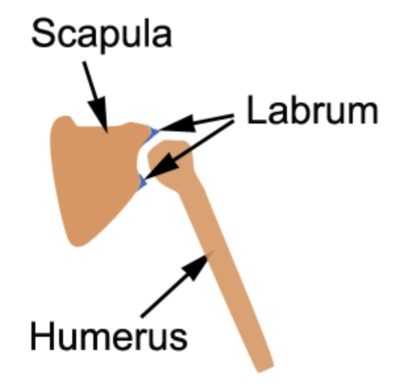
Figure 2 – Shoulder Labrum Anatomy

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Elbow
Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
Tearing of the medial collateral ligament of the elbow (figure 6) typically following an excessive or repetitive sideways force to the elbow (valgus force – figure 7), such as throwing (particularly with poor technique). Associated with pain on firmly touching the affected ligament (at the inner aspect of the elbow) and often swelling. A snap or tear may be audible during injury.
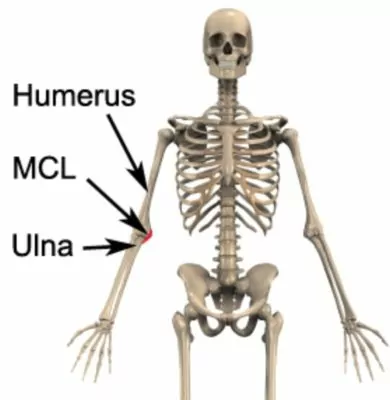
Figure 6 – Medial Collateral Ligament of the Elbow (MCL)
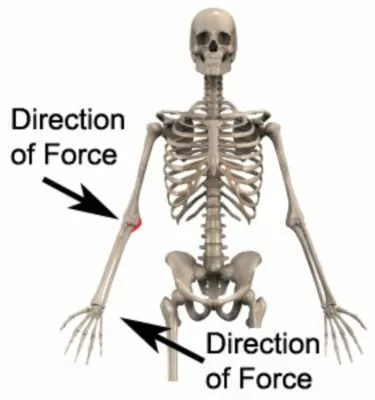
Figure 7 – Valgus Force to the Elbow

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Upper Back & Chest
Stress Fracture of the 1st Rib
Stress fracture of the first rib bone typically due to overuse associated with excessive muscle traction on the ribs during activities such as throwing. Typically associated with a dull ache in the shoulder, upper back, chest or lower neck (often near the collar bone) and tenderness on firmly touching the localised area of bone. Pain is usually worse with activity (e.g. throwing) and eases with rest.
 Contributing Factors to Throwing Injuries
Contributing Factors to Throwing Injuries
A number of factors may contribute to the development of throwing injuries, including:
- Overuse (excessive or inappropriate training, i.e. throwing too often or for too long)
- Poor throwing biomechanics (i.e. poor technique)
- Inadequate upper limb and shoulder flexibility (particularly shoulder flexion, abduction, external or internal rotation)
- Muscle tightness (particularly the latissimus dorsi, pectorals, rotator cuff, abdominals & hip flexors)
- Inadequate thoracic spine flexibility (particularly into extension and rotation)
- Joint stiffness (particularly the shoulder, elbow, upper back, lower back and hips)

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
 Injury Prevention Tips for Throwing Athletes
Injury Prevention Tips for Throwing Athletes
Correct Throwing Technique
Ensure your throwing technique is safe and efficient, minimising the risk of injury to the shoulder and elbow. Make sure you use the whole body, including the legs and hips rather than confining the throwing motion to the upper body.
Some key throwing technique tips include:

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Warm Up the Shoulder
One of the best ways to prevent throwing related shoulder injuries is with an effective warm up before sport. Shoulder exercises using resistance band helps activate the important stabilizing muscles, such as the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers, and helps improve proprioception in preparation for throwing (see Upper Limb Resistance Band Exercises). Once you start throwing, ease into it. Avoid going straight into hard and fast or long throws. Gradually increase the distance and speed of the throws to allow your shoulder and elbow to warm up.
Flexibility
Ensuring adequate flexibility is important to improve your throwing technique and thus reduce the risk of injury. Key joints which require adequate range of motion for throwing include:
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Upper Back
- Lower Back
- Hips
Flexibility exercises for these body parts, and the muscles surrounding them, are an important aspect of injury prevention for throwers. Massage Therapy to these areas can also play a key role in maintaining adequate range of movement (see Upper Body and Lower Body Massage Ball Exercises).
Upper back (thoracic) flexibility (particularly extension and rotation) is extremely important for throwing athletes. Not only does this help with injury prevention to the shoulder, but it also assists in enhanced throwing performance. Exercises using a foam roller can help improve upper back flexibility (see Upper Back Flexibility Exercises).
Core Stability & Conditioning
In land based throwing sports, a stable pelvis, trunk and shoulder blade are essential to minimize stress on the shoulder and elbow, and, to improve throwing performance. Many throwing injuries can be attributed to poor strength or activation of the core stabilisers, such as the gluteals, scapular stabilisers, rotator cuff, transverses abdominis, obliques, multifidus and pelvic floor. As part of your training, ensure you spend enough time working on improving your gluteal strength, core stability, rotator cuff strength and scapular stability (see Core Stability Exercises, Pilates Exercises, Rotator Cuff Exercises, Gluteal Strengthening Exercises, and Scapular Stability Exercises).

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
 Physiotherapy Products for Throwing Injuries
Physiotherapy Products for Throwing Injuries
The following physiotherapy products are commonly prescribed to patients by physiotherapists to assist in the rehabilitation and prevention of throwing injuries:
To purchase physiotherapy products to assist with injury rehabilitation click on one of the above links or visit the PhysioAdvisor Shop.
 Find a Physio
Find a Physio
Find a physiotherapist in your local area who can treat throwing injuries.
 More Exercises
More Exercises
- View Core Stability Exercises.
- View Pilates Exercises.
- View Rotator Cuff Exercises.
- View Gluteal Strengthening Exercises.
- View Scapular Stability Exercises.
- View Shoulder Stretches.
- View Upper Back Stretches.
- View Elbow Stretches.
- View Leg Stretches.

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/injury-diagnosis/sports-injuries/throwing-injuries-2”>Throwing Injuries – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>PhysioAdvisor provides detailed physiotherapy information on throwing injuries including most common throwing injuries, contributing factors and injury prevention tips.
Return to the top of Throwing Injuries.






