Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dislocation
Updated:
(Also known as Tibialis Posterior Tendon Subluxation)
What is tibialis posterior tendon dislocation?
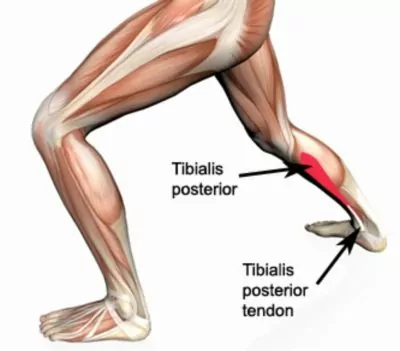
The tibialis posterior muscle originates from the back of the tibia and fibula (lower leg bones), it then travels down along the inside of your leg and ankle where it inserts into various bones in the foot via the tibialis posterior tendon (figure 1). The tibialis posterior tendon is held firmly in place at the level of the ankle by strong connective tissue known as the tibialis posterior retinaculum. Occasionally this retinaculum can be torn due to strong contraction of the tibialis posterior muscle. As a result, the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle is free to move in and out of its original position and may flick over the bony prominence at the inside of the ankle. This condition is known as a tibialis posterior tendon dislocation.
Signs and symptoms of tibialis posterior tendon dislocation
Patients with this condition typically experience inner ankle pain and stiffness with local bruising and swelling. Patients may be unable to weight bear and may experience a flicking sensation at the inside of the ankle with certain ankle movements. Pain may also increase on firmly touching the tibialis posterior tendon.
Diagnosis of tibialis posterior tendon dislocation
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist may be all that is necessary to diagnose tibialis posterior tendon dislocation. Diagnosis may be confirmed with an MRI scan or ultrasound investigation.
Treatment for tibialis posterior tendon dislocation
All patients who potentially have a tibialis posterior tendon dislocation should see a physiotherapist or doctor immediately so their condition can be assessed and the likelihood of them having a tibialis posterior tendon dislocation determined. This is important as delayed treatment may result in a poor outcome. Meanwhile, initial injury management in the first 48 – 72 hours is vital to reduce bleeding, swelling and inflammation. This should comprise of rest from aggravating activity (crutches are often required), regular icing, the use of a compression bandage and elevation of the affected limb. Anti-inflammatory medication may also be useful in this early phase as guided by the treating doctor or pharmacist.
Immediate surgical relocation of the tibialis posterior tendon and reconstruction of the retinaculum is indicated in patients who have a tibialis posterior tendon dislocation. This is important to ensure optimal function of the foot and ankle. Following surgery, a period of immobilization in either a plaster cast or protective boot is likely.
It is also important for patients to perform pain free flexibility, strengthening and balance exercises to ensure an optimal outcome once the surgeon has indicated that is it safe to do so. The treating physiotherapist can advise which exercises are most appropriate for the patient and when they should be commenced. Rehabilitation of these injuries usually takes 6 months or longer with intensive physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy for tibialis posterior tendon dislocation
Physiotherapy treatment is vital to hasten healing and ensure an optimal outcome in all patients with this condition. Treatment may comprise:
- soft tissue massage
- electrotherapy (e.g. ultrasound)
- anti-inflammatory advice
- stretches
- joint mobilization
- taping or bracing
- the use of crutches
- ice or heat treatment
- exercises to improve flexibility, strength and balance
- education
- activity modification advice
- biomechanical correction
- footwear advice
- a gradual return to activity program
Ankle exercises
- View Ankle Stretches.
- View Ankle Strengthening Exercises.
- View Balance Exercises.
Physiotherapy products for tibialis posterior tendon dislocation
Some of the most commonly recommended products by physiotherapists for patients with this condition include:
To purchase physiotherapy products for tibialis posterior tendon dislocation click on one of the above links or visit the PhysioAdvisor Shop.
Find a Physio for Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dislocation
Find a Physiotherapist in your local area who can treat this condition.

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/ankle/tibialis-posterior-tendon-dislocation”>Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dislocation – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>PhysioAdvisor offers detailed physiotherapy information on tibialis posterior tendon dislocation including: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, physiotherapy products and more...
Return to the top of Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dislocation.