Tibial Stress Fracture
Updated:
(Also known as Stress Fracture of the Tibia, Medial Tibial Stress Fracture)
What is a tibial stress fracture?
A tibial stress fracture is a condition that is primarily characterised by an incomplete break in the lower leg / shin bone (tibia) (figure 1).
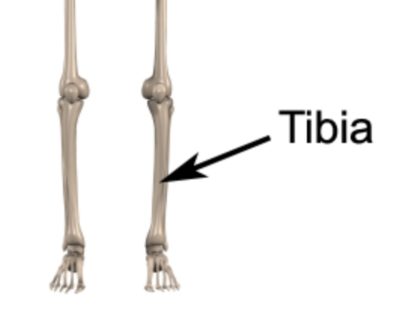
During weight-bearing activity (such as running), compressive forces are placed through the tibia. In addition, several muscles attach to the tibia, so that when they contract, a pulling force is exerted on the bone. When these forces are excessive, or too repetitive, and beyond what the bone can withstand, bony damage can gradually occur. This initially results in a bony stress reaction, however, with continued damage may progress to a tibial stress fracture.
Causes of a tibial stress fracture
A stress fracture of the tibia is an overuse injury that typically develops gradually over time due to activities placing large amounts of stress through the tibia beyond what it can withstand. These activities usually involve excessive weight bearing activity such as running, sprinting or jumping. The condition often occurs following a recent increase in activity or change in training conditions.
Signs and symptoms of a tibial stress fracture
Patients with this condition typically experience a gradual onset of localized pain at the inner aspect of the shin bone. The pain is often sharp or acute in nature and typically increases with impact activity and decreases with rest. Occasionally pain may be felt with rest or even at night. In severe cases, walking may be enough to aggravate symptoms. Patients with this condition typically experience tenderness on firmly touching the inner aspect of the shin bone. Occasionally, a tibial stress fracture may present as calf pain or pain located at the front of the shin (rather than the inner aspect of the bone).
Diagnosis of a tibial stress fracture
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist may be sufficient to diagnose a tibial stress fracture. Further investigations such as an X-ray, bone scan and CT scan are usually required to confirm diagnosis and determine the severity of injury.
Treatment for a tibial stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Contributing factors to the development of a tibial stress fracture
There are several factors that may contribute to the development of this condition. These need to be assessed and corrected with direction from a physiotherapist. Some of these factors include:
- inappropriate or excessive training (particularly on hard or uneven surfaces)
- poor foot posture (particularly excessively high arches or flat feet)
- poor biomechanics
- muscle weakness
- muscle fatigue
- muscle tightness (particularly of the calf muscles)
- joint stiffness (particularly of the ankle)
- inappropriate footwear
- inappropriate running technique
- inadequate diet
- leg length discrepancies
- being overweight
- menstrual disturbances
Physiotherapy for a tibial stress fracture
Physiotherapy treatment for patients with this condition is vital in to hasten the healing process, ensure an optimal outcome and reduce the likelihood of injury recurrence. Treatment may comprise:
- soft tissue massage (particularly to the calf muscles)
- joint mobilization (particularly to the ankle)
- electrotherapy (e.g. ultrasound)
- dry needling
- the use of crutches
- the use of an appropriate brace
- activity modification advice
- arch support taping
- biomechanical correction (e.g. the prescription of orthotics)
- exercises to improve strength, balance, flexibility and cardiovascular fitness
- hydrotherapy
- education
- a gradual return to activity plan
- correct footwear advice
Prognosis of a tibial stress fracture
Most patients with this condition heal well with appropriate physiotherapy and return to activity or sport in approximately 8 – 12 weeks. In patients with more severe stress fractures a full recovery may take 3 – 6 months or longer. Early physiotherapy treatment is vital to hasten recovery and ensure an optimal outcome.
Other intervention for a tibial stress fracture
Despite appropriate physiotherapy management, some patients with this condition do not improve and require other intervention to ensure an optimal outcome. The treating physiotherapist or doctor can advise on the best course of management when this is the case. This may include further investigations such as X-rays, bone scan, CT scan or MRI, extended periods of non-weight bearing or immobilization or use of an appropriate brace, review with a podiatrist for orthotics or referral to appropriate medical authorities who can advise on any intervention that may be appropriate to improve the condition. In rare cases that are not responsive to an appropriate physiotherapy program, surgical intervention may be indicated.
Exercises for a tibial stress fracture
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with a stress fracture of the tibia. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 – 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms.
Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms.
Initial Exercises
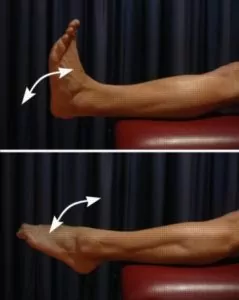
Foot and ankle up and down
Move your foot and ankle up and down as far as possible and comfortable without pain (figure 2). Repeat 10 – 20 times provided there is no increase in symptoms.
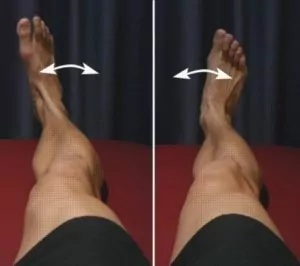
Foot and ankle in and out
Move your foot and ankle in and out as far as possible and comfortable without pain (figure 3). Repeat 10 – 20 times provided there is no increase in symptoms.
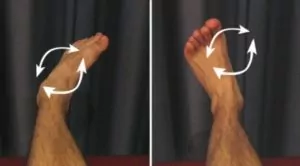
Foot and Ankle Circles
Move your foot and ankle in a circle as large as possible and comfortable without pain (figure 4). Repeat 10 – 20 times in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions provided there is no increase in symptoms.
Intermediate Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Advanced Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Rehabilitation Protocol for a tibial stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
 Find a Physio for a tibial stress fracture
Find a Physio for a tibial stress fracture
Find a physiotherapist in your local area who can treat a stress fracture of the tibia.
 Physiotherapy products for a tibial stress fracture
Physiotherapy products for a tibial stress fracture
Some of the most commonly recommended products by physiotherapists for patients with this condition include:
-
 Wheat Bags
Wheat Bags -
 AllCare Ortho Total Ankle Brace (AOA19)
AllCare Ortho Total Ankle Brace (AOA19) -
 Forearm Crutches Adjustable – Standard Grip
Forearm Crutches Adjustable – Standard Grip -
 AllCare Wobble Board (Red – ACWOBRD)
AllCare Wobble Board (Red – ACWOBRD) -
 AllCare Band
AllCare Band -
 AllCare Tubing
AllCare Tubing -
 AllCare Spikey Massage Ball
AllCare Spikey Massage Ball -
 AllCare Instant Cold Pack (15 x 25cm)
AllCare Instant Cold Pack (15 x 25cm) -
 Lournet Stability Dura Disc
Lournet Stability Dura Disc -
 AllCare Ortho Standard Walker (Cam Boot)
AllCare Ortho Standard Walker (Cam Boot) -
 Thermoskin Heat Retaining Ankle Wrap
Thermoskin Heat Retaining Ankle Wrap
To purchase physiotherapy products for a stress fracture of the tibia click on one of the above links or visit the PhysioAdvisor Shop.
 More information
More information
- Ankle Stretches.
- Ankle Strengthening Exercises.
- Calf Stretches.
- Calf Strengthening Exercises.
- Leg Stretches.
- Leg Strengthening Exercises.
- Balance Exercises
- How to use Crutches
- Choosing a Shoe.
- Do I need orthotics?.
- Ice or Heat
- R.I.C.E. Regime.
- Return to Running Program.
- Return to Sport.
- Why is my Injury not Improving?
- Foot Taping.
- Lower Leg Diagnosis Guide.
Become a PhysioAdvisor Member

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/lower-leg/tibial-stress-fracture”>Tibial Stress Fracture – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>PhysioAdvisor offers detailed physiotherapy information on a tibial stress fracture including: diagnosis, treatment, exercises, physiotherapy products and more...
Return to the top of Tibial Stress Fracture.


