Rib Stress Fracture
Updated:
(Also known as a Stress Fracture of the Rib)
What is a rib stress fracture?
A rib stress fracture is a relatively uncommon injury comprising an incomplete crack in one (or more) rib bones.
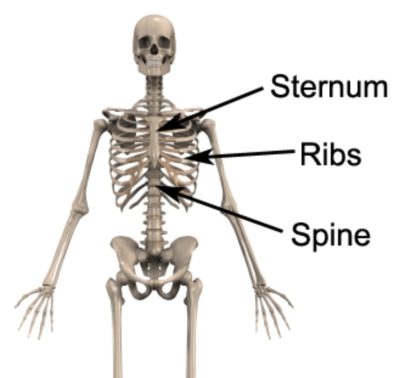
The rib cage consists of twelve ribs located on either side of the upper back and chest. Each individual rib bone originates from the spine, connecting to a vertebrae in the centre of the upper back and then curves around the side of the body to the chest (at the front of the body – figure 1). The upper seven rib bones connect with the sternum at the front of the chest, the next three ribs (i.e. ribs 8 to 10) join with the above ribs via cartilage tissue, whilst ribs 11 and 12 remain unattached at the front of the body and therefore are commonly known as ‘floating ribs’.
Numerous muscles of the abdomen, shoulder girdle and back attach to one or more ribs. As these muscles contract or are placed on stretch, a pulling or tensile force is exerted on the rib bones. If these forces are excessive due to too much repetitive, prolonged or high force damage to one or more of the rib bones may occur. The initial bony damage associated with these stresses typically involves a bony stress reaction. With ongoing participation in damaging activities, the condition may deteriorate and eventually progress to a rib stress fracture.
Stress fractures of the first rib are occasionally seen in baseball pitchers or tennis players, whilst stress fractures of the fourth and fifth ribs are often seen in rowers.
Cause of a rib stress fracture
Rib stress fractures usually occur gradually over a period of time due to excessive muscle traction on the ribs associated with overuse. Although uncommon, this may be seen in throwing sports (such as baseball pitchers), overhead sports (such as tennis players) or in paddling sports (such as rowers or kayakers).
When a rib stress fracture occurs, it is frequently in association with a sudden increase in activity or recent change in stresses on the affected rib. Sometimes, this may be associated with training technique modifications or training condition changes. In less common cases, a rib stress fracture may occur traumatically. This may occur in contact sports from a collision or due to a fall onto a hard object or the ground.
Signs and symptoms of a rib stress fracture
A stress fracture of the rib typically causes a localised pain in the chest or upper back that increases with exercise and activities placing strain on the affected rib (e.g. rowing, throwing, twisting, bumping or lying on the ribs). Often the patient may have to stop activity due to the pain. Pain usually decreases with rest.
Occasionally, pain may radiate into the back, neck, side of the ribs or shoulder. In more severe cases, breathing deeply, laughing, sneezing or coughing may also provoke symptoms. Symptoms typically increase when firmly touching the affected region of the bone and occasionally night ache or swelling may also be present.
Diagnosis of a rib stress fracture
Diagnosis of this condition usually begins with a thorough examination by a physiotherapist or doctor. Radiological investigations such as an X-ray, CT scan, MRI or bone scan are typically necessary to confirm diagnosis and evaluate the injury severity and presence of other conditions.
Prognosis of a rib stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Treatment for a rib stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Contributing factors to the development of a rib stress fracture
A number of factors may work in isolation or combination, contributing to the onset of a rib stress fracture. For an optimal outcome, it is vital that these factors are identified and where possible, corrected under physiotherapy guidance. These factors may comprise:
- muscle weakness
- poor flexibility
- joint stiffness (particularly of the upper back, shoulder or neck)
- poor posture
- inadequate diet
- excessive or inappropriate training or activity
- insufficient rest periods from training or activity
- poor training technique
- sudden training changes
- menstrual disturbance in females
- fatigue
- a lack of fitness or conditioning
Physiotherapy for a rib stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Other intervention for a rib stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Exercises for a rib stress fracture
The exercises below are often prescribed to patients with a stress fracture of one or more ribs. The suitability of these exercises should be discussed with your treating physiotherapist prior to commencement. In general, the exercises should be performed three times per day provided they do not provoke or increase symptoms.
Your treating physiotherapist can advise when you should begin the initial exercises and progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a rule of thumb, progression or addition of exercises should only occur provided there is no exacerbation of symptoms.
Initial Exercises
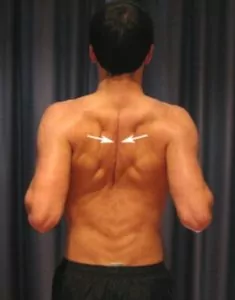
Shoulder Blade Squeezes
Start by standing in optimal posture with your back and neck straight (figure 2). Slowly squeeze your shoulder blades together as far as possible without discomfort, ensuring you experience no greater than a moderate stretch. Hold for two seconds and repeat ten times provided the exercise does not cause or increase symptoms.
Deep Breaths
Sit or stand in optimal posture with your back and neck straight (figure 3). Take a deep breath, breathing in as deeply as possible without provoking symptoms and then release. Focus on diaphragmatic breathing – using your lower lungs (without elevating your shoulders) allowing your stomach to gently expand and recede. Perform 5 breaths.
Rotation in Sitting
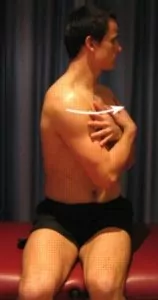
Begin this exercise by sitting in optimal posture, with a straight back and neck and your arms across your chest. Gently turn your body to one side as far as possible without discomfort, ensuring you feel no more than a moderate stretch (figure 4). Try to keep your legs still throughout the exercise. Hold for two seconds and repeat ten times to each side provided there is no increase in symptoms.
Intermediate Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Advanced Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Rehabilitation Protocol for a rib stress fracture

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now

Physiotherapy products for a rib stress fracture
Some products that are often recommended by physiotherapists to optimise healing and recovery in patients with a stress fracture of the rib include:
To purchase physiotherapist recommended products for a stress fracture of the rib, click on the relevant link above or visit the PhysioAdvisor Shop.
 Find a Physio for a rib stress fracture
Find a Physio for a rib stress fracture
Find a physiotherapist in your local area who can treat patients with this condition.

Other Exercises
- Upper Back Stretches.
- Upper Back Strengthening Exercises.
- Core Stability Exercises.
- Scapular Stability Exercises.
- Pilates Exercises.
- Postural Exercises.
 More Information
More Information
- Initial Injury Management / R.I.C.E. Regime.
- Posture.
- Posture Taping.
- Ice or Heat?
- Warming Up and Cooling Down.
- Returning to Running.
- Returning to Sport.
- Upper Back & Chest Diagnosis Guide.
- Why is my injury not improving?
Become a PhysioAdvisor Member

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/upper-back-chest/rib-stress-fracture”>Rib Stress Fracture – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>PhysioAdvisor offers detailed physiotherapy information on a rib stress fracture including: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, exercises, physiotherapy products and more...
Return to the top of Rib Stress Fracture.