Triceps Tendonitis
Updated:
(Also known as Tricep Tendonitis, Tricep Tendinopathy, Tricep Tendinitis, Tricep Tendinosis)
N.B. Although research suggests that ‘triceps tendinopathy’ is the more appropriate term to describe overuse injuries to the triceps tendon, we will use the term ‘triceps tendonitis’ in this document as it is more widely known.
What is triceps tendonitis?
Triceps tendonitis is a condition characterized by tissue damage to the triceps tendon causing pain in the back of the elbow.
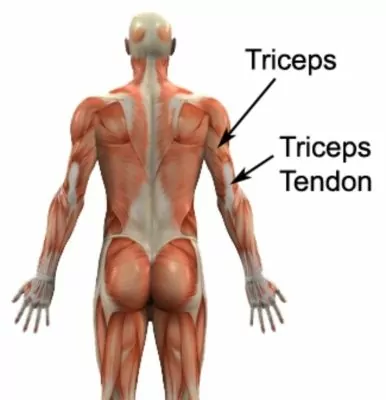
The muscle at the back of the upper arm is known as the triceps. The triceps originates from the shoulder blade and humerus (upper arm bone) and inserts into the ulna (forearm bone) via the triceps tendon (figure 1).
The triceps muscle is primarily responsible for straightening the elbow and assisting certain shoulder movements. During contraction of the triceps, tension is placed through the triceps tendon. When this tension is excessive due to too much repetition or high force, damage to the triceps tendon may occur. Triceps tendonitis is a condition whereby there is damage to the triceps tendon with subsequent degeneration and inflammation. This may occur traumatically due to a high force going through the triceps tendon beyond what it can withstand, or more commonly, due to gradual wear and tear associated with overuse.
Causes of triceps tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the triceps tendon. This typically occurs due to repetitive pushing activities or straightening the elbow against resistance (such as performing push ups or dips). Occasionally, it may occur suddenly due to a high force going through the triceps tendon beyond what it can withstand. This most commonly occurs during heavy weight lifting in a gym environment.
Signs and symptoms of triceps tendonitis
Patients with this condition typically experience pain in the back of the elbow. In less severe cases, patients may only experience an ache or stiffness in the elbow that increases with rest following activities requiring strong or repetitive contraction of the triceps muscle. These activities may include performing push ups, bench presses or dips, using a hammer repetitively or punching excessively (e.g. boxing).
In more severe cases, patients may experience an ache that increases to a sharper pain with activity. Occasionally patients may notice swelling at the back of the elbow and experience weakness when attempting to straighten the elbow against resistance and pain or tightness when performing a triceps stretch. Pain may also increase when firmly touching the affected triceps tendon (figure 1).
Diagnosis of triceps tendonitis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose triceps tendonitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an ultrasound, X-ray, CT scan or MRI scan may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Prognosis of triceps tendonitis
Most patients with this condition heal well with appropriate physiotherapy and return to normal function in a number of weeks. Occasionally, rehabilitation can take significantly longer and may take many months in those who have had the condition for a long period of time. Early physiotherapy treatment is vital to hasten recovery.
Treatment for triceps tendonitis

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Contributing factors to the development of triceps tendonitis
There are several factors which can predispose patients to developing this condition. These need to be assessed and corrected with direction from a physiotherapist. Some of these factors include:
- joint stiffness (particularly the elbow)
- muscle tightness (particularly the triceps)
- inappropriate or excessive training
- inadequate warm up
- muscle weakness
- inadequate recovery between training sessions
- inadequate rehabilitation following a previous elbow injury
- a history of neck or upper back injury
- being overweight
Physiotherapy for triceps tendonitis
Physiotherapy treatment for patients with this condition is vital to hasten the healing process, ensure an optimal outcome and reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Treatment may comprise:
- soft tissue massage
- electrotherapy (e.g. ultrasound)
- stretches
- joint mobilization
- elbow taping
- dry needling
- ice or heat treatment
- exercises to improve strength and flexibility
- education
- anti-inflammatory advice
- activity modification advice
- a gradual return to activity program
Other intervention for triceps tendonitis
Despite appropriate physiotherapy management, some patients with this condition do not improve adequately. When this occurs the treating physiotherapist or doctor will advise on the best course of management. This may include further investigations such as X-rays, ultrasound, MRI or CT scan, pharmaceutical intervention, corticosteroid injection, autologous blood injections or referral to appropriate medical authorities who will advise on any interventions that may be appropriate to improve the condition.
Exercises for triceps tendonitis
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 – 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms.
Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate, advanced and other exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms.
Initial Exercises
Elbow Bend to Straighten
Bend and straighten your elbow as far as possible pain free (figure 1). Repeat 10 – 20 times provided there is no increase in symptoms.
Static Triceps Contraction
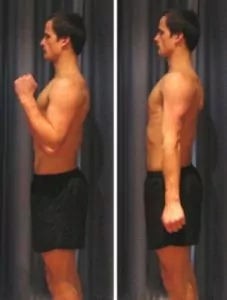
Begin this exercise with your elbow at your side and bent to 90 degrees (figure 3). Your palm should be facing inwards with your hand in a fist as demonstrated. Push down against your other hand tightening the muscles at the back of your arm (triceps). Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times as hard as you can go without pain.
Intermediate Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Advanced Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Other Exercises

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
Rehabilitation Protocol for triceps tendonitis

Members Only ContentBecome a PhysioAdvisor Member to gain full access to this exclusive content. For more details see Become a Member. Already a member? Login Now
 Find a Physio
Find a Physio
Find a physiotherapist in your local area who can treat patients with this condition.
 Physiotherapy products for triceps tendonitis
Physiotherapy products for triceps tendonitis
Some of the most commonly recommended products by physiotherapists for patients with this condition include:
To purchase physiotherapy products for triceps tendonitis click on one of the above links or visit the PhysioAdvisor Shop.
 More Information
More Information
- Triceps Stretches.
- Triceps Strengthening Exercises
- Elbow Strengthening Exercises.
- Elbow Stretches.
- Elbow Taping.
- View detailed information about when to use Ice or Heat.
- Read more about initial injury management and the R.I.C.E. Regime.
- View detailed information on when to Return to Sport.
- View our Elbow & Forearm Diagnosis Guide.
Become a PhysioAdvisor Member
-
 Individual Membership (12 Months)$59.95 for 1 year
Individual Membership (12 Months)$59.95 for 1 year -
 Individual Membership (3 Months)$39.95 for 3 months
Individual Membership (3 Months)$39.95 for 3 months -
 Individual Membership (Yearly)$49.95 / year
Individual Membership (Yearly)$49.95 / year -
 Individual Membership (Monthly)$15.95 / month
Individual Membership (Monthly)$15.95 / month

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/injuries/elbow-forearm/triceps-tendonitis”>Triceps Tendonitis – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>PhysioAdvisor offers expert physiotherapy information on tricep tendonitis including symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, exercises and products.
Return to the top of Triceps Tendonitis.