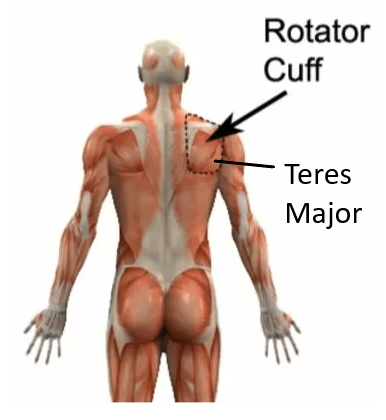
Teres Major Anatomy: Understanding Structure and Function
Updated:
The teres major is a crucial muscle in the shoulder region that plays a significant role in upper limb movements and stability. This article provides a comprehensive overview of teres major anatomy, covering its origin, insertion, action, function, nerve supply, blood supply, palpation techniques, clinical relevance, common injuries, and includes a list of useful links to relevant articles on www.physioadvisor.com.au for a deeper understanding.
Teres Major Anatomy
- Origin: The teres major originates from the inferior angle of the scapula, in close proximity to the insertion point of the rhomboid major muscle.
- Insertion: This muscle inserts into the medial lip of the intertubercular groove of the humerus, near the insertion of the latissimus dorsi muscle.
- Action: The primary function of the teres major is to medially rotate and adduct the arm. Additionally, it assists in extending the arm from a flexed position, aiding in actions such as climbing or lifting heavy objects.
- Function: Working in conjunction with other shoulder muscles, the teres major facilitates smooth and controlled movements during various upper limb activities, ensuring optimal shoulder function.
Nerve Supply and Blood Supply:
The teres major muscle is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve (C5-C7) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It receives its blood supply primarily from branches of the subscapular artery.
Teres Major Anatomy Palpation
Palpating the teres major is an essential technique for clinicians to assess its condition and identify potential issues. To palpate the teres major, the patient should be in a seated or lying position, with the arm slightly adducted and medially rotated. The muscle can be located along the inferior angle of the scapula, and its tendon can be felt as it attaches to the humerus.
Clinical Relevance:
- Common Injuries: The teres major, like other shoulder muscles, is susceptible to injuries, particularly during activities involving repetitive arm movements or heavy lifting. Common injuries may include strains, tears (see rotator cuff tear), and overuse-related problems (e.g. rotator cuff tendinopathy), leading to pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
- Shoulder Instability: In cases of shoulder instability or dislocation, the teres major, along with other shoulder muscles, may be affected, contributing to functional limitations.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): In rare cases, the teres major may play a role in the development of frozen shoulder, a condition characterized by pain and restricted shoulder mobility.
Useful Links:
- Rotator Cuff Tear – Rehabilitation and treatment
- Rotator Cuff Tendonitis – Physiotherapy management
- Teres Major Strengthening Exercises
- Shoulder Stretching Exercises
- Shoulder Strengthening Exercises
- Understanding Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
In conclusion, a sound understanding of teres major anatomy is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to optimize their shoulder health. Its role in medially rotating and adducting the arm makes it a key player in various upper limb activities. Practicing proper warm-up routines, adopting ergonomic techniques, and seeking professional advice in case of injuries can promote teres major muscle health and overall shoulder well-being. Remember, an informed approach to shoulder care is vital for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle.
Teres Major Anatomy References:
- Teres Major Muscle by KenHub
- Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
- Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray’
- Standring S. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016.
- Anatomy for Students. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2019.

Link to this Page
If you would like to link to this article on your website, simply copy the code below and add it to your page:
<a href="https://physioadvisor.com.au/teres-major-anatomy-understanding-structure-and-function”>Teres Major Anatomy: Understanding Structure and Function – PhysioAdvisor.com</a><br/>Learn about teres major anatomy including, origin ,insertion, action, nerve supply, blood supply, palpation, common injuries and more...
Return to the top of Teres Major Anatomy: Understanding Structure and Function.
